The MongoDB architecture is structured horizontally into three main layers: the MongoDB Client, the MongoDB Server, and the Disk.
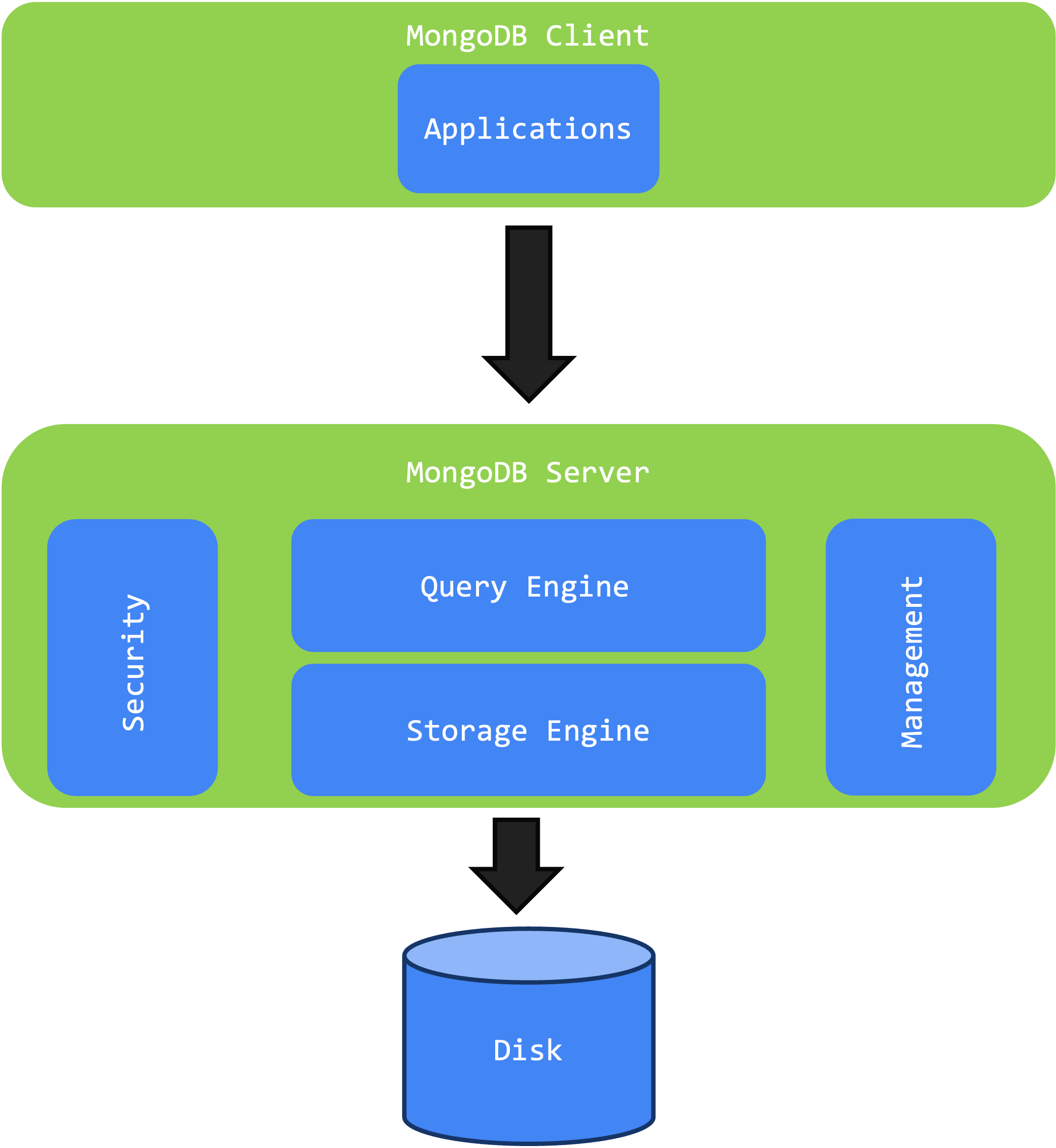
1.2.1. Architecture
Client
- Applications: This top layer consists of applications that interact with MongoDB. These client applications send data requests to the server and handle the responses. They utilize MongoDB drivers and libraries to communicate with the database, performing operations like inserting, querying, updating, and deleting data.
Server
- Security: This module handles authentication and authorization, ensuring that only authorized users and applications can access the database. It implements security policies to protect data against unauthorized access and attacks.
- Query Engine: The query engine processes and executes database queries received from client applications. It optimizes query performance and determines the most efficient way to retrieve or modify data.
- Storage Engine: This component is responsible for the actual storage and retrieval of data. It manages how data is written to and read from the disk, ensuring efficient data access and integrity.
- Management: The management layer supports administrative tasks such as monitoring, backup, recovery, and system scaling. It helps maintain the overall performance and reliability of the database system.
Disk
- The disk layer represents the physical storage where data is persistently stored. The storage engine writes data to the disk and retrieves it for queries, ensuring data durability and availability.
1.2.2. Components
MongoDB stores data records as documents (specifically BSON documents), which are gathered together in collections. A database stores one or more collections of documents.
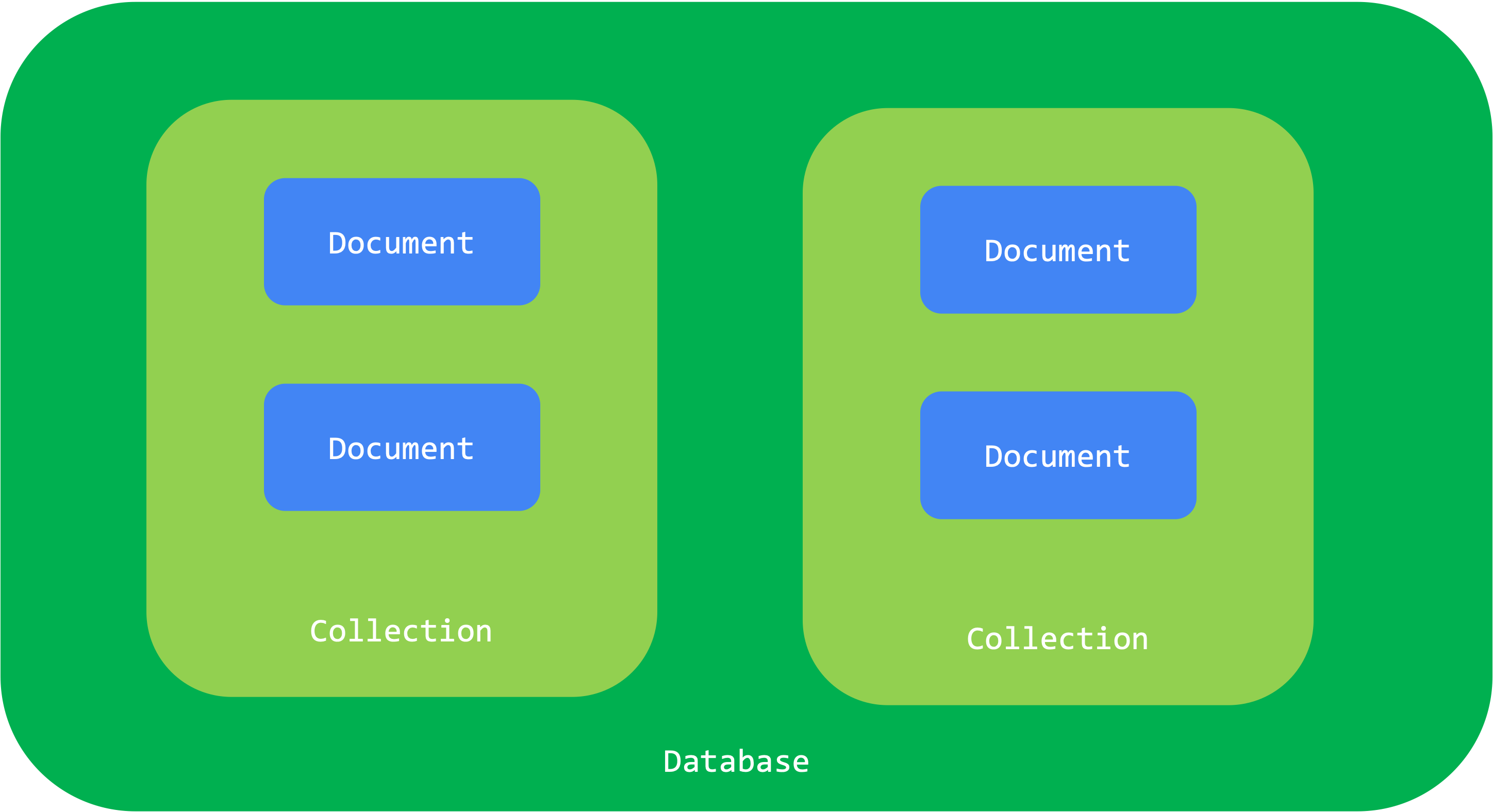
Collections & Documents
In MongoDB, a collection is a fundamental component that contains a set of documents. Collections do not need to exist before inserting a document. When you add the first document to a collection, MongoDB automatically creates the collection if it doesn’t already exist.
A document in MongoDB is a set of key-value pairs and serves as the primary building block of data. Documents are represented in JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) format, which aligns with MongoDB’s schema-less design.
Data is stored in BSON (Binary JSON), a binary representation of JSON documents. BSON is used because it supports more data types than JSON, including various data types, documents, and arrays.
Because documents can be large, MongoDB sometimes compresses them to reduce their size further, although this is not always the case.
Users create collections to hold multiple documents. Since MongoDB is a schema-less database, collections can store documents with different fields. This flexibility allows users to insert documents with fields that have never existed in any previous document within the collection.